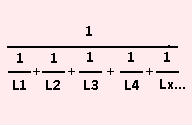
The formula for inductors in parallel:
 When AC is applied to a coil, a varying magnetic field will be produced around it. When another coil is placed within that magnetic field, it will induce a current flowing in that coil. This principle is called MUTUAL INDUCTANCE
When AC is applied to a coil, a varying magnetic field will be produced around it. When another coil is placed within that magnetic field, it will induce a current flowing in that coil. This principle is called MUTUAL INDUCTANCE
The amount of mutual inductance between the two coils depends on the distance between the two coils, and the angle between the two coils. When two coils are linked together via mutual inductance in this manner, we say that the coils are inductively COUPLED.
When the mutually inductive coils are close to each other, we say that they are closely, or tightly coupled. When they are far apart, we say that they are loosely coupled. The greatest amount of coupling occurs when the coils are wound one directly over the other and on a closed iron core. The quantity of coupling between two coils is sometimes referred to as the Coefficient of Coupling. The formula for Coefficient of Coupling is:
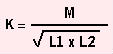
Inductance is an opposition to the flow of current in an AC circuit by a coil. This is caused by the expanding and collapsing of the magnetic field. More important though, as the field expands and collapses, it generates a counter- electromotive force, by way of mutual inductance within the same coil. We call this SELF INDUCTANCE.
Simply put, self inductance is when a coils magnetic field, produces an electric current within the same coil. This self inductance causes a resistance to AC current. But this resistance is not measured in Ohms, as normal resistance is. This resistance isn’t even called resistance, it’s called REACTANCE, because of the way it reacts with AC. In the case of a coil, it is specifically called INDUCTIVE REACTANCE, and it’s symbol is XL.
XL is a very special number!
XL is the variable number that we use while expressing the AC resistance of a coil.
MEMORIZE THIS FORMULA:
XL= 2pfL
Where:
f = the FREQUENCY in Hz
L= the inductance of the coil in henries and
p= 3.1415926536….. (or 3.14 for short)