 Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing.
Frequency modulation (FM) is the encoding of information in a carrier wave by varying the instantaneous frequency of the wave. The technology is used in telecommunications, radio broadcasting, signal processing, and computing.
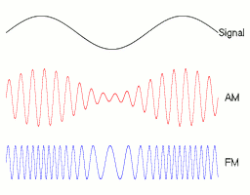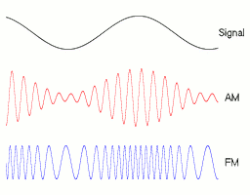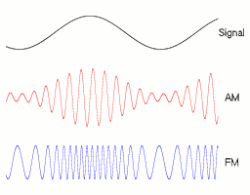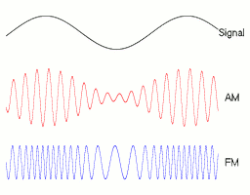
In analog frequency modulation, such as radio broadcasting, of an audio signal representing voice or music, the instantaneous frequency deviation, i.e. the difference between the frequency of the carrier and its center frequency, has a functional relation to the modulating signal amplitude.
Digital data can be encoded and transmitted with a type of frequency modulation known as frequency-shift keying (FSK), in which the instantaneous frequency of the carrier is shifted among a set of frequencies. The frequencies may represent digits, such as ‘0’ and ‘1’. FSK is widely used in computer modems, such as fax modems, telephone caller ID systems, garage door openers, and other low-frequency transmissions. Radioteletype also uses FSK.
Frequency modulation is widely used for FM radio broadcasting. It is also used in telemetry, radar, seismic prospecting, and monitoring newborns for seizures via EEG,[3] two-way radio systems, sound synthesis, magnetic tape-recording systems and some video-transmission systems. In radio transmission, an advantage of frequency modulation is that it has a larger signal-to-noise ratio and therefore rejects radio frequency interference better than an equal power amplitude modulation (AM) signal. For this reason, most music is broadcast over FM radio. (wikipedia)
Slope Detection:
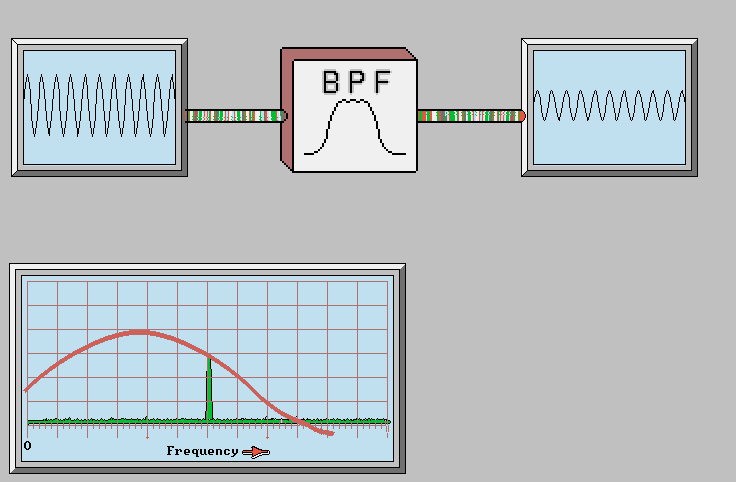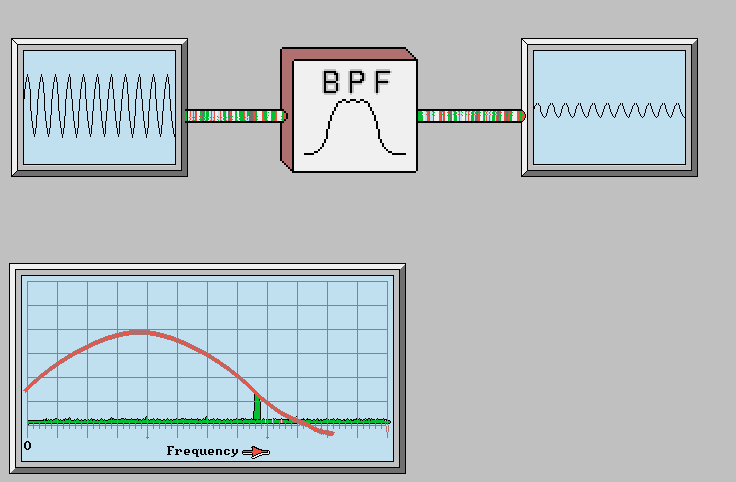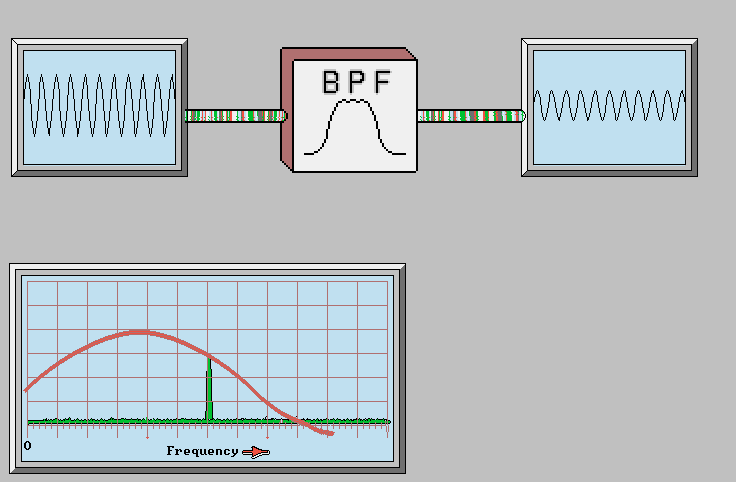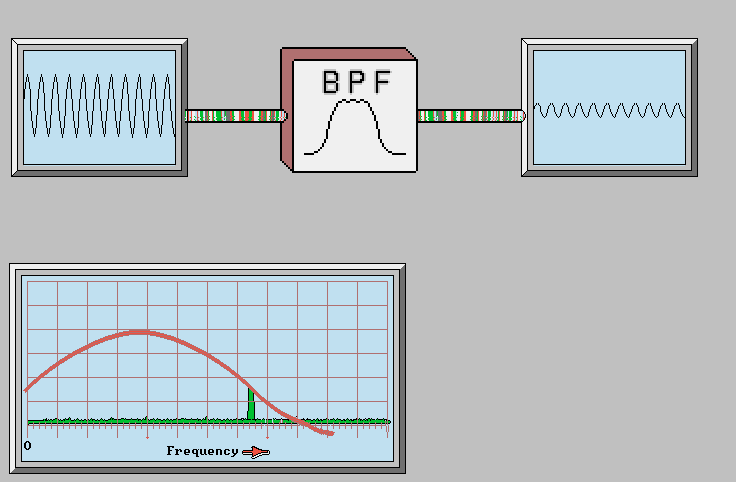
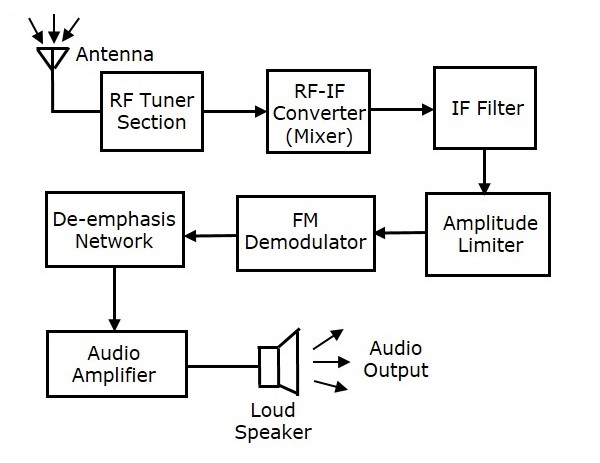
FM Receiver Block Diagram: