What is it? kv4p HT is a homebrew Open Source VHF radio that can turn your android mobile phone capable of voice and text communication completely off-grid. At least a Technician class amateur radio license. The radio simply plugs into the USB C port on your Android...
Trending Now
Kits
Apps
Design
Gallery
Reviews
Downloads
Weather Station coming up
We will be installing a weather station in this area. You will be able to see local temperature, humidity, wind direction and wind speed.
Maxwell’s Equations
Quantities and units. Electricity is a difficult substance to appreciate with the human senses. About the only way you get a feeling for it is to moisten the tongue and apply it between the terminals of a 9 volt battery. Of course, you get more idea if you are...
The Latest
kv4p HT – Turn Your Android phone into Modern Ham Radio transceiver
What is it? kv4p HT is a homebrew Open Source VHF radio that can turn your android mobile phone capable of voice and text communication completely off-grid. At least a Technician class amateur radio license. The radio simply plugs into the USB C port on your Android...
IC 555 Tutorial
The 555 timer IC was first introduced around 1971 by the Signetics Corporation as the SE555/NE555 and was called "The IC Time Machine" and was also the very first and only commercial timer ic available. It provided circuit designers and hobby tinkerers with a...

FoxDelta Ham Radio Kits by VU2FD
Explore Your Favorite Topics
Ham Radio and Electronics Articles, Downloads, Circuit Designs and Solutions
Transciver
WalkieTalkie
Microphone
Monitor
Antenna
Power Supply
Cables
Components
Kits
Buy Sell
Business Ventures
kv4p HT – Turn Your Android phone into Modern Ham Radio transceiver
What is it? kv4p HT is a homebrew Open Source VHF radio that can turn your android mobile phone capable of voice and text communication completely off-grid. At least a Technician class amateur radio license. The radio simply plugs into the USB C port on your Android...
Weather Station coming up
We will be installing a weather station in this area. You will be able to see local temperature, humidity, wind direction and wind speed.
Staff Picks
kv4p HT – Turn Your Android phone into Modern Ham Radio transceiver
What is it? kv4p HT is a homebrew Open Source VHF radio that can turn your android mobile phone capable of voice and text communication completely off-grid. At least a Technician class amateur radio license. The radio simply plugs into the USB C port on your Android...
Weather Station coming up
We will be installing a weather station in this area. You will be able to see local temperature, humidity, wind direction and wind speed.
Maxwell’s Equations
Quantities and units. Electricity is a difficult substance to appreciate with the human senses. About the only way you get a feeling for it is to moisten the tongue and apply it between the terminals of a 9 volt battery. Of course, you get more idea if you are...
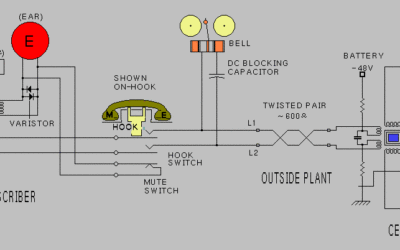
Telephone System
Semiconductors: Diodes and Transistors
Semiconductors: Diodes & Transistors In the early days of electricity there were only two groups of material: insulators and conductors. Insulators are matters, which do not allow the flow of electric current through them. Glass, porcelain, dry air and dry wood...
FM Detector
FM stands for Frequency Modulation. It means that the RF-frequency will change according to the input audio signal. Example: A FM radio signal at 105.1MHz will not be exactly stable at 105.1MHz, The audio signal in the RF will modulate (change) the frequency for about...
Product Reviews
Weather Station coming up
We will be installing a weather station in this area. You will be able to see local temperature, humidity, wind direction and wind speed.
Maxwell’s Equations
Quantities and units. Electricity is a difficult substance to appreciate with the human senses. About the only way you get a feeling for it is to moisten the tongue and apply it between the terminals of a 9 volt battery. Of course, you get more idea if you are...
Telephone System
Stay Up to Date With The Latest News & Updates
Access Premium Content
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque
Join Our Newsletter
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque
Follow Us
Follow Us on other platforms